您所在的位置:首页 - 新能源 - 正文新能源
中国新能源车企故事
![]() 奚诗科技
05-01
【新能源】
60人已围观
奚诗科技
05-01
【新能源】
60人已围观
摘要**Title:SchematicDiagramofNewEnergyVehiclesbyTraditionalAutomotiveCompanies**Traditionalautomotiveco
Title: Schematic Diagram of New Energy Vehicles by Traditional Automotive Companies
Traditional automotive companies are increasingly delving into the realm of new energy vehicles (NEVs), driven by environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. NEVs encompass electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and plugin hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), each utilizing distinct propulsion systems. Below is a schematic diagram outlining the basic principles of these NEVs as adopted by traditional automotive manufacturers.
Schematic Diagram: New Energy Vehicles (NEVs)
1. Electric Vehicle (EV)
Electric vehicles are solely powered by electricity stored in onboard batteries. They eliminate tailpipe emissions and are considered zeroemission vehicles.
Components:
Battery Pack
: Stores electrical energy and powers the electric motor.
Electric Motor
: Converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle.
Power Electronics
: Manages the flow of electricity between the battery and the motor, controlling speed and torque.
Charger
: Converts AC power from the grid into DC power to recharge the battery pack.
Onboard Charger
: Controls the charging process and regulates the flow of electricity from the grid to the battery.Operation:
1.
Charging
: The EV is plugged into a charging station, and the onboard charger converts AC electricity from the grid into DC electricity to recharge the battery pack.2.
Driving
: The battery pack supplies electricity to the electric motor, which drives the wheels, providing propulsion. When the battery depletes, the vehicle needs to be recharged.2. Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
Hybrid electric vehicles combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric propulsion system. They can operate on electricity, gasoline, or a combination of both.
Components:
Battery Pack
: Stores electrical energy for the electric motor.
Electric Motor/Generator
: Assists the internal combustion engine during acceleration and recaptures energy during braking, acting as a generator to recharge the battery.
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
: Burns gasoline to generate power and drive the wheels directly or charge the battery indirectly through the generator.
Power Split Device
: Mechanism that controls power distribution between the ICE, electric motor, and wheels.
Power Electronics
: Manages the flow of electricity between the battery, electric motor, and generator.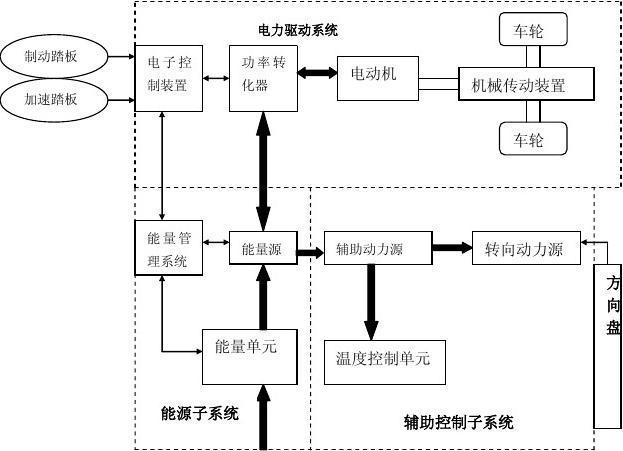
Operation:
1.
Electric Mode
: At low speeds or when cruising, the vehicle operates solely on electric power, drawing energy from the battery pack.2.
Hybrid Mode
: During acceleration or when more power is required, the internal combustion engine kicks in, supplementing the electric motor.3.
Regenerative Braking
: When decelerating or braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electricity to recharge the battery pack.3. Plugin Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
Plugin hybrid electric vehicles are similar to HEVs but feature larger battery packs that can be recharged by plugging into an external power source.
Components:
Battery Pack
: Larger capacity than conventional hybrids, allowing for extended electriconly driving range.
Electric Motor/Generator
: Provides propulsion and assists the internal combustion engine when needed.
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
: Provides additional power and acts as a range extender when the battery depletes.
Charger
: Allows the vehicle to recharge its battery pack from an external power source.
Power Electronics
: Controls the flow of electricity between the battery, electric motor, generator, and charging port.Operation:
1.
Electric Mode
: The vehicle can operate solely on electric power for a certain distance, depending on the battery capacity, before the internal combustion engine engages.2.
Hybrid Mode
: When the battery depletes or additional power is needed, the internal combustion engine supplements the electric motor, providing propulsion.3.
Charging
: The battery pack can be recharged by plugging the vehicle into a charging station or wall outlet, allowing for extended electriconly driving range.This schematic diagram provides a simplified overview of the key components and operation principles of new energy vehicles developed by traditional automotive companies. As technology evolves, these systems continue to advance, offering more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
Tags: 新能源汽车和传统车的区别 传统车企为什么不开发新能源 传统车企转型新能源 新能源车传动系统 传统车企的新能源车
上一篇: 金夫人婚纱摄影各地的套餐价格都一样吗
下一篇: 武汉青少年宫